Manufacturing most cyberattacked industry, says IBM Security

Ransomware is the top cyber-attack type in North America in 2021, phishing is the attack mode of choice, and manufacturing is the country’s most attacked industry – these are just some of the security trends observed throughout 2021 and reported in the just-released IBM Security 2022 X-Force Threat Intelligence Index.
The global report has been put together by the IBM Security X-Force, an in-house team of cybersecurity experts and remediators who have mined billions of data points to expose today’s most urgent security statistics and trends.
Here, we outline the top 10 takeaways for North American organisations.
1. North America was third-most attacked region in the world in 2021
North America was the third-most attacked region in the world in 2021, behind Europe and Asia-Pacific, receiving 23% of all cyberattacks tracked by IBM’s X-Force team.
2. Ransomware is top cyber-attack type
Like Europe, ransomware led as the top attack type on North American organisations last year, making up 30% of all attacks in this region, although it decreased as a share of overall attacks, perhaps because of law enforcement action, reports IBM. It’s possible that the increased law enforcement activity in 2021, including the takedown of botnets and ransomware groups, are beginning to impede the attack rate traditionally observed in the region. The REvil operation made up a whopping 43% of the ransomware attacks observed in North America (37% globally) before the gang was shut down in October 2021. Members of the gang were arrested, but many ransomware groups that disband later re-emerge under new names. LockBit 2.0., Conti, CryptoLocker and Eking were other ransomware attacks observed. IBM recommends having a ransomware response plan, backups and alternate location for critical business operations during remediation. Consider if or when you might ever pay a ransom.
3. Business email compromise attackers renewed assault on North American organisations
Business email compromise (BEC) was the second-most common attack type in North America in 2021, making up 12% of attacks and suggesting the BEC attackers have renewed their assault on North American organisations, looking to compromise those that do not have multi-factor authentication (MFA) deployed. According to IBM, MFA can decrease the risk of several types of attack, including ransomware, data theft, business email compromise (BEC) and server access. X-Force research confirms that zero trust principles can decrease organisations’ susceptibility to BEC. Identity and access management technologies are making MFA implementation easier.
4. Phishing is attack mode of choice in North America
Phishing appears to be the attack vector of choice for threat actors targeting North America, observed in nearly half (47%) of the incidents that X-Force remediated in this region in 2021. The brands that were most imitated in phishing kits are among the largest and most trusted companies – Microsoft, Apple and Google. Vulnerability exploitation came in second at 29%, and removable media (12%), brute force (9%) and stolen credentials (9%) were also used. According to the report, threat actors may be focused on phishing as move North American organisations implement robust patch management programs in the face of several critical vulnerabilities released in 2020 and 2021.
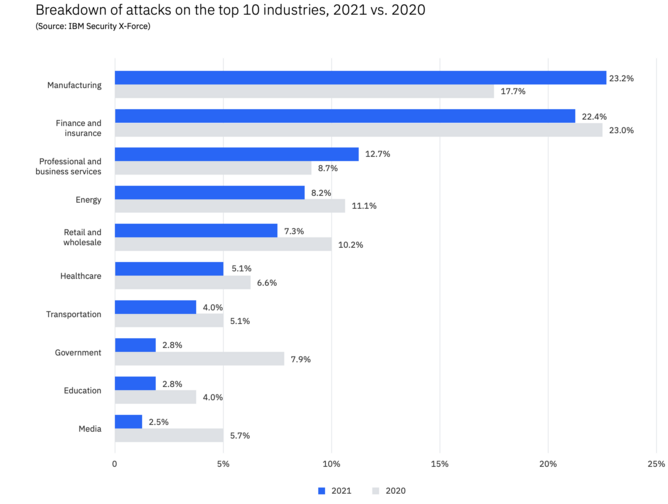
5. Manufacturing is North America’s most attacked industry
For the first time in five years, manufacturing outpaced finance and insurance globally in the number of cyberattacks levied against these industries, and was the top-attacked industry in North America too, constituting 28% of all attacks. This attack rate is probably associated with the significant supply chain-related strain on manufacturing emerging from the pandemic. One in four attacks on this sector are from ransomware. Manufacturers have a low tolerance for downtime, and ransomware actors are capitalising on operational stressors exacerbated by the pandemic. Threat actors understand the critical role manufacturing plays in global supply chains and are seeking to disrupt these organisations.
6. Professional services and wholesale are attractive targets for ransomware
Professional and business services also proved attractive targets for cyberattacks in North America in 2021, second after manufacturing constituting 15% of all cyberattacks, followed by retail and wholesale at 11%. Manufacturing, professional and wholesale are all attractive targets for ransomware actors possibly due to their low tolerance for downtime and sensitive client data on their networks that – if stolen and threatened to be leaked – can put intense pressure on a victim to pay a ransom.
7. Surge in IoT malware activity
As defences to cyberattacks grow stronger, malware is getting more innovative, sophisticated new tricks to infiltrate. The report reveals a 3,000% surge in IoT malware activity between Q3 2019 and Q4 2020. Attackers are increasingly using cloud-based messaging and storage services to blend into legitimate traffic. And some groups are experimenting with new techniques in encryption and code obfuscation to go unnoticed. IBM suggests maintaining properly hardened systems, enacting effective password policies and ensuring policy compliance is critical to maintaining a robust cloud security posture.
8. Vulnerabilities rise sharply as the IoT expands
The number of vulnerabilities related to IoT devices increased 16% year over year, compared to a growth rate of only 0.4% for vulnerabilities overall. For industrial control systems, the rise was even more dramatic at 50%, an elevated risk as threat actors seek to disrupt the manufacturing and energy sectors. So, while industrial organisations are certainly at the greatest risk, any organisation using IoT is increasingly exposed to vulnerabilities.
9. As organisations move to the cloud, attackers follow
Malware targeting Linux environments rose dramatically in 2021, a surge possibly correlated to more organisations moving into cloud-based environments, many of which rely on Linux for their operations. According to IBM’s X-Force team, a gang called LemonDuck caused several compromises observed by X-Force in 2021. LemonDuck malware evolved from crypto mining and has since built a large botnet of compromised devices; it targets both Linux and Windows systems. LemonDuck campaigns capitalise on news events for phishing lures. The surging level of new and unique code in Linux malware in 2021, compared to 2020, highlights how innovation in Linux malware has made these threats more dangerous.
10. More ransomware attacks in May and June
The frequency of ransomware attacks tends to shift throughout the year, often increasing in May and June. Ransomware attacks appear to decrease in late summer or early fall, with January having the least amount of activity.
- Microsoft and Tech Mahindra share cybersecurity insightsTechnology & AI
- Five Minutes With: Kelly Ahuja, CEO at Versa NetworksLeadership & Strategy
- How to align cybersecurity and business objectivesLeadership & Strategy
- IBM and EY's AI-powered solution is set to transform HRTechnology & AI






